Sambucus racemosa
Red-berried elder description:
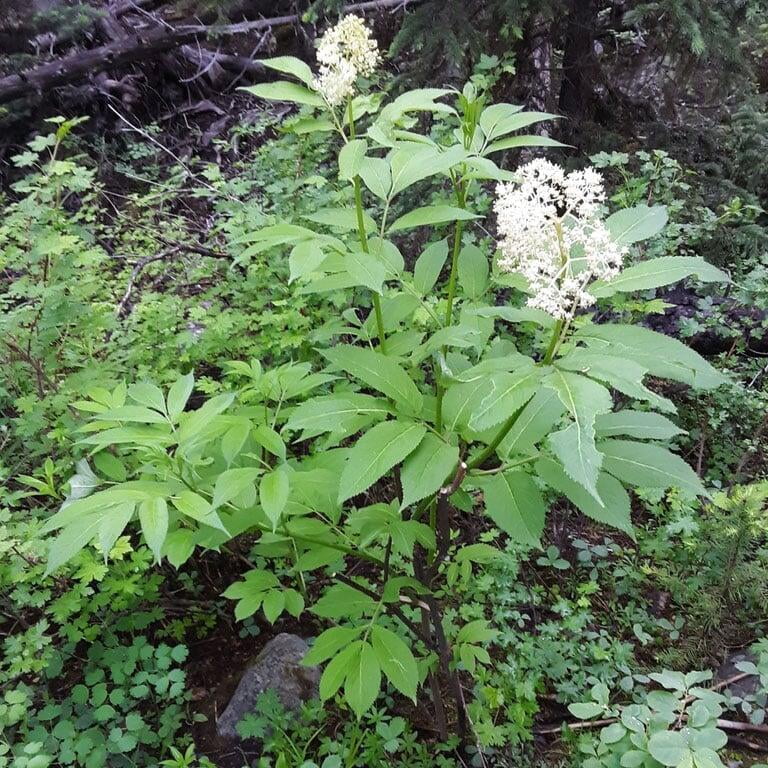
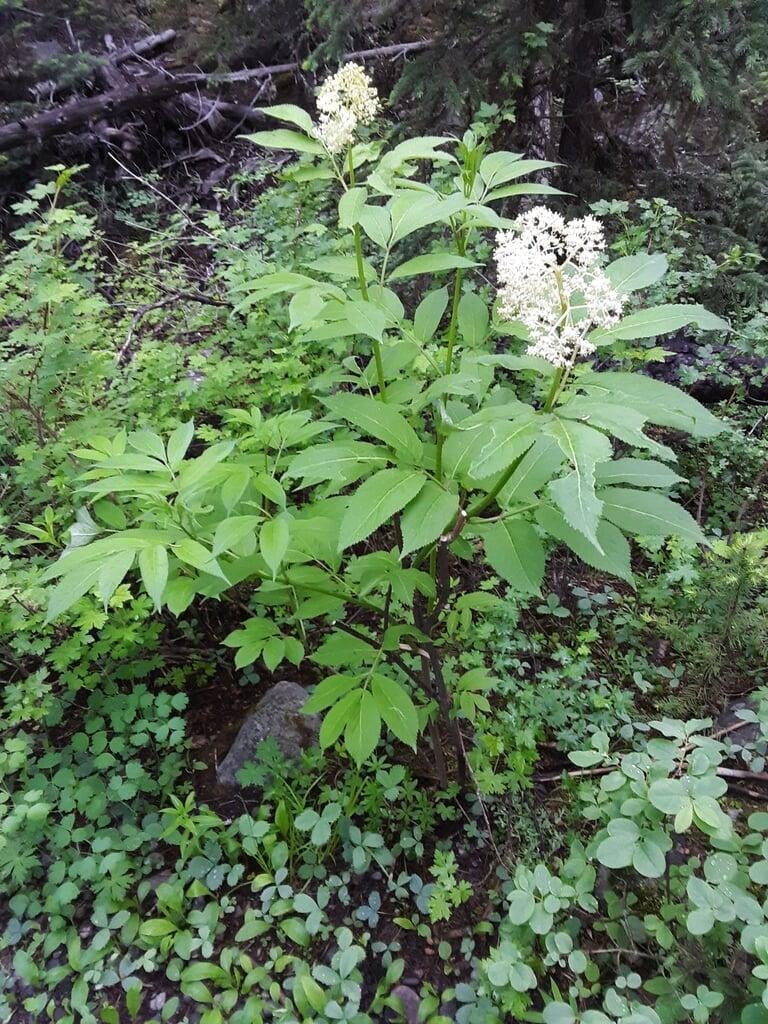
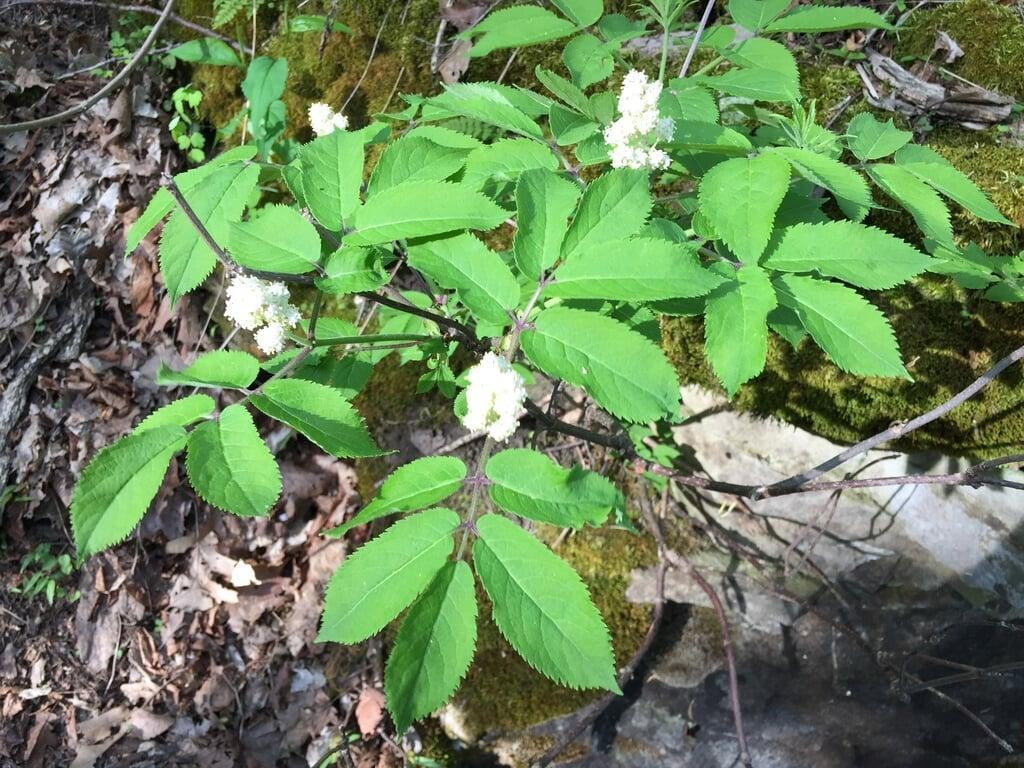
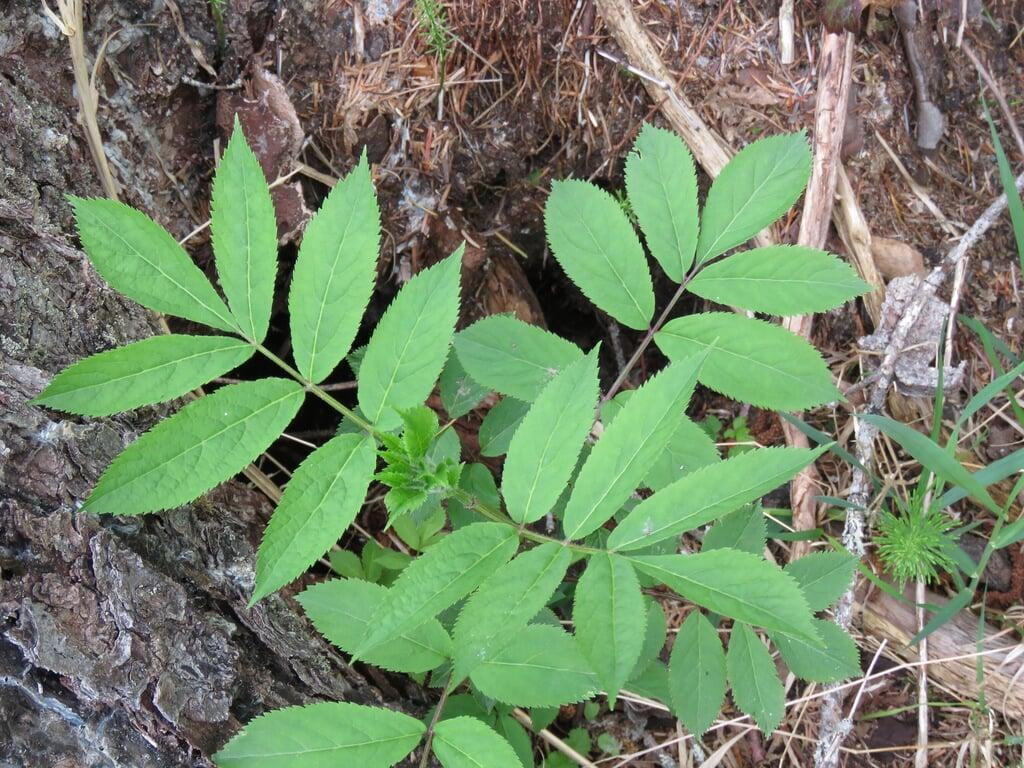
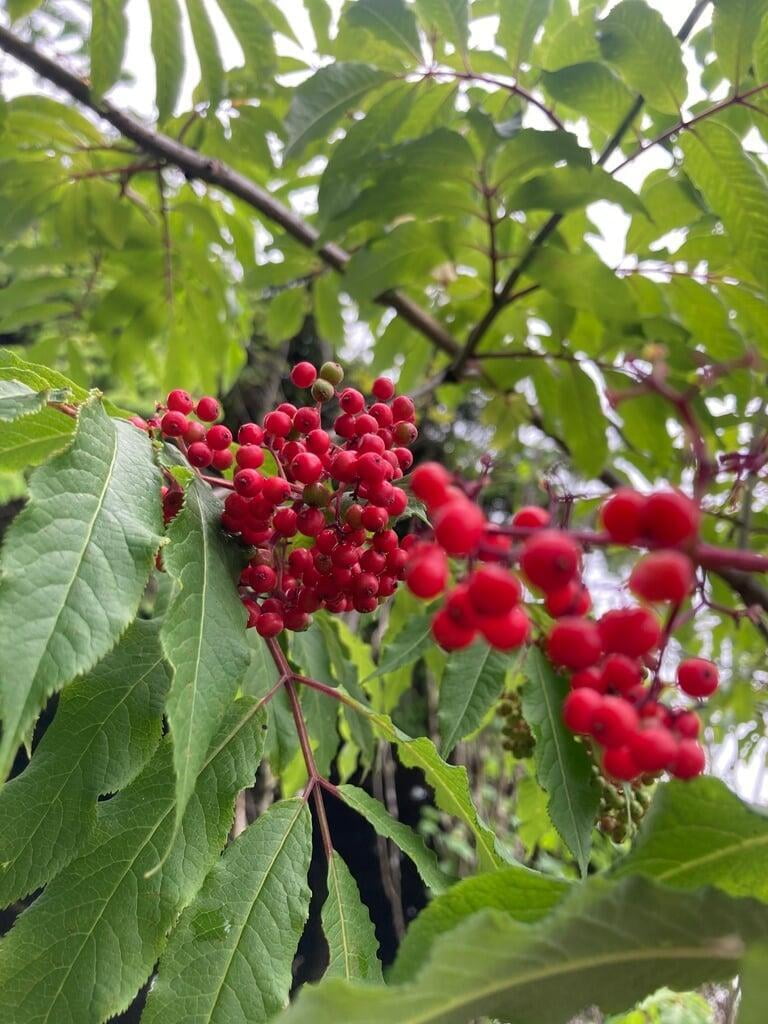
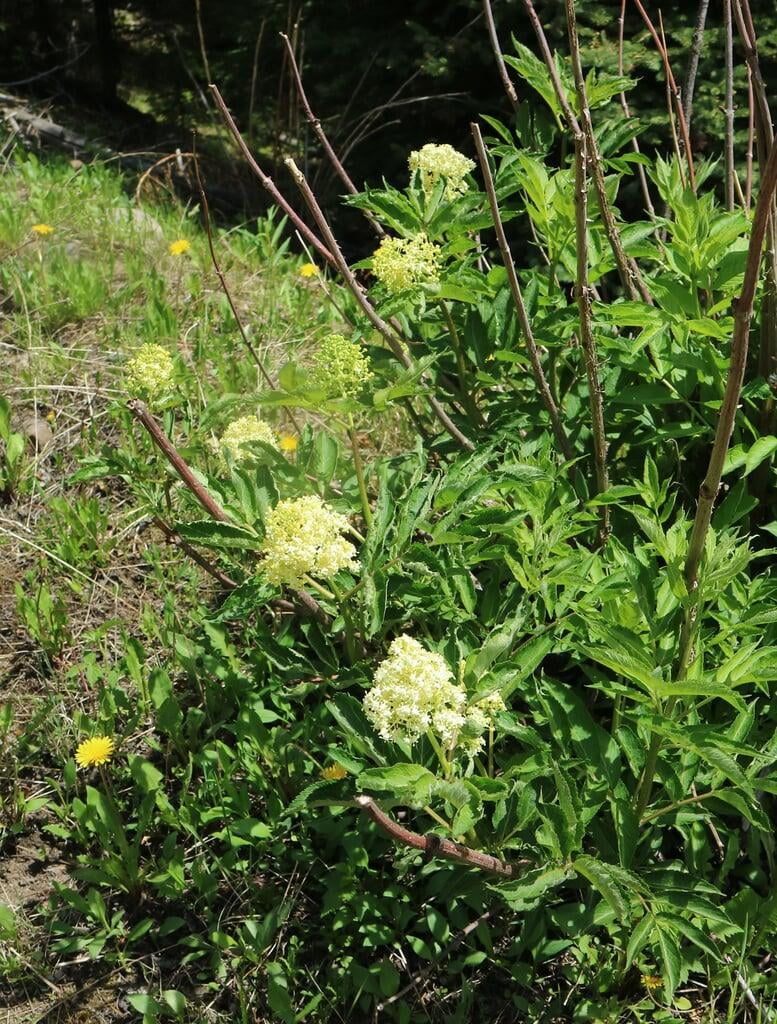
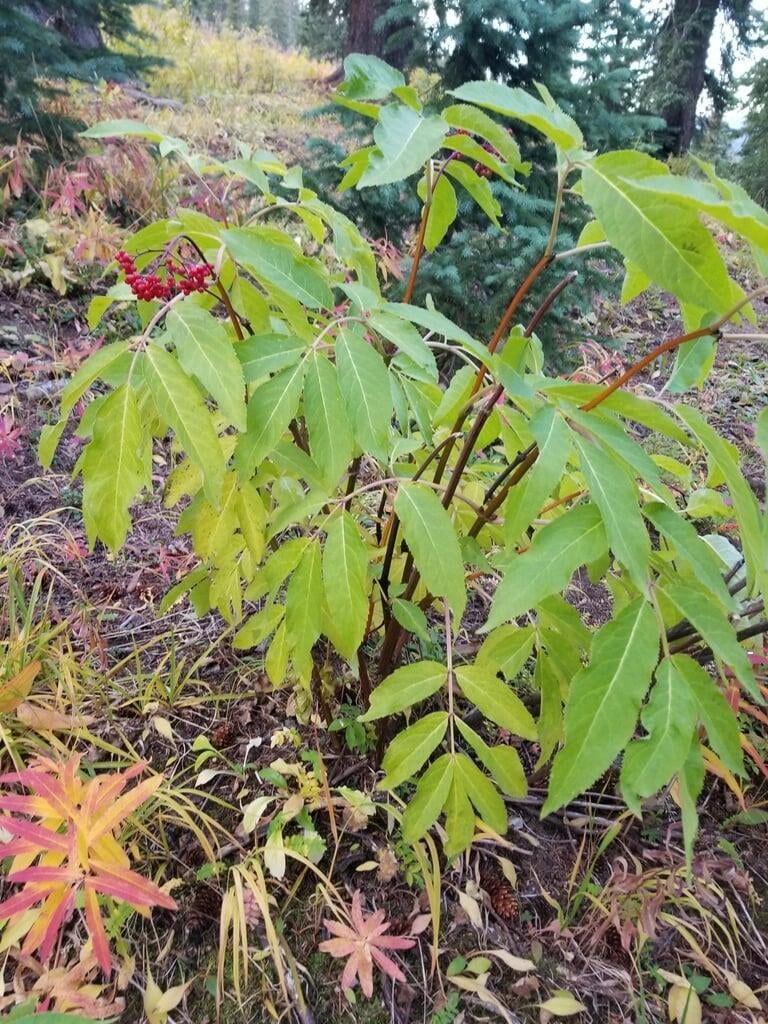
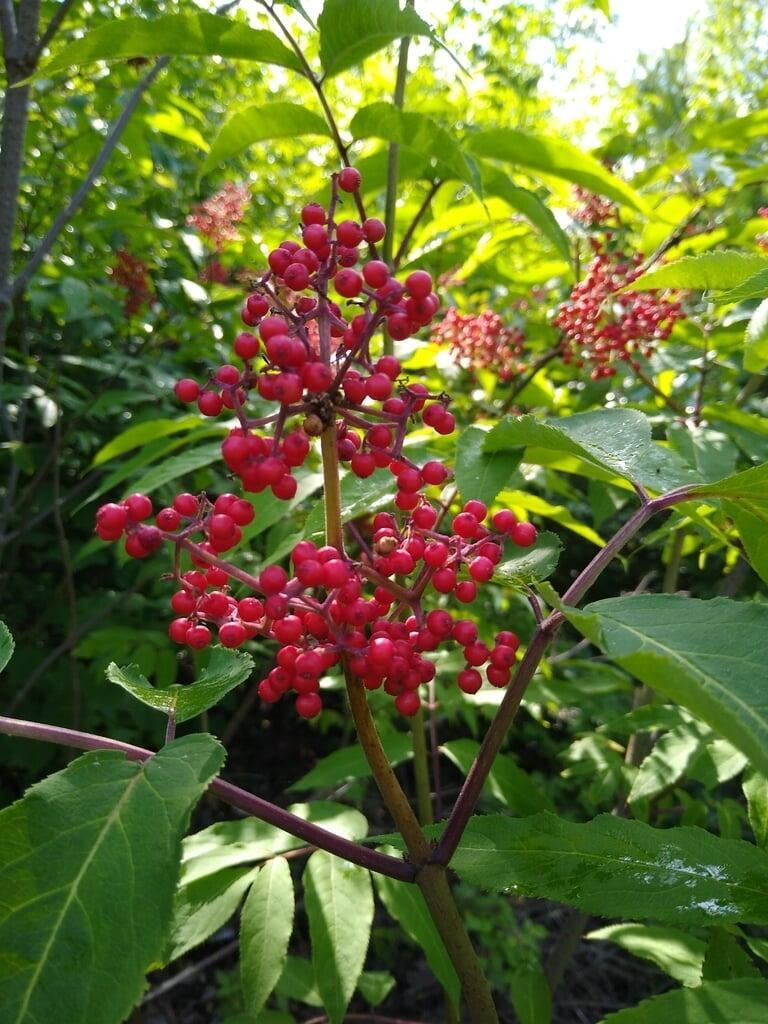
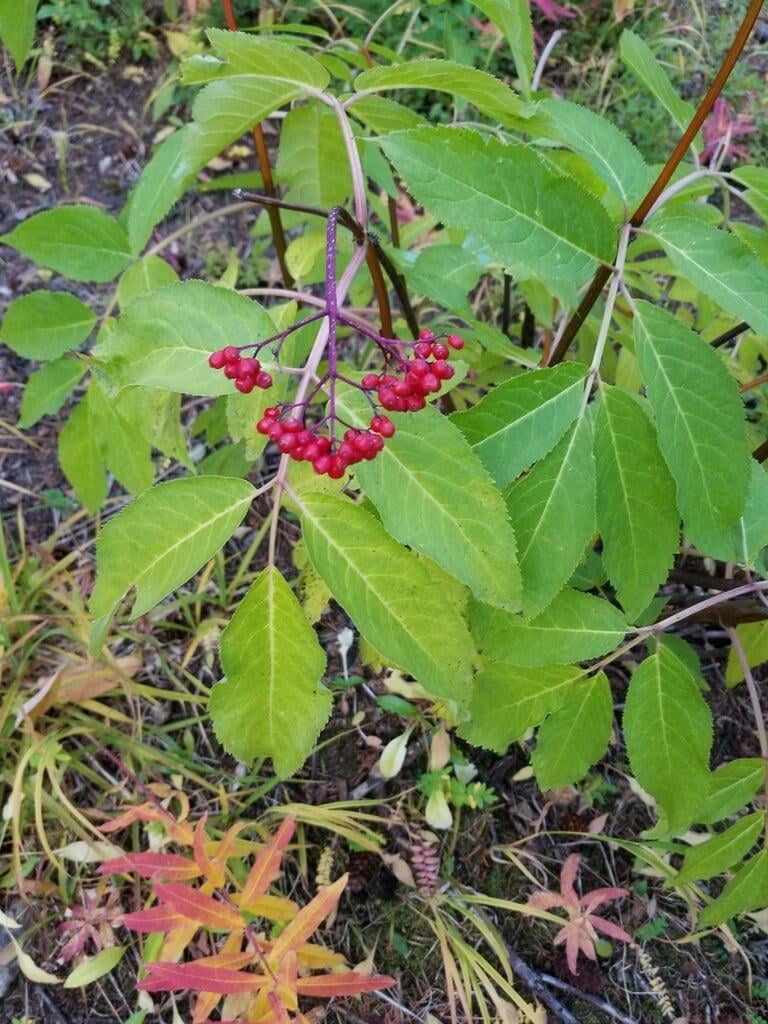
Sambucus racemosa, commonly known as red elderberry or red-berried elder, is a deciduous shrub native to North America. It typically grows to a height of 14 feet and a width of 6-12 feet. The plant has a multi-stemmed growth habit and produces large clusters of bright red berries in the summer. The leaves are pinnately compound, with 5-9 leaflets, and have a distinctive saw-toothed edge.
Red elderberry is typically found in moist, forested areas at low to mid elevations. It is a popular food source for a variety of wildlife, including birds, bears, and small mammals. The berries can also be used to make jams, jellies, and syrups.
While red elderberry can be a striking addition to a garden or landscape, it should be noted that all parts of the plant are toxic if ingested. Care should be taken when handling the plant, as contact with the leaves or berries can cause skin irritation. Additionally, the shrub has a tendency to sucker and can spread aggressively if not properly maintained.
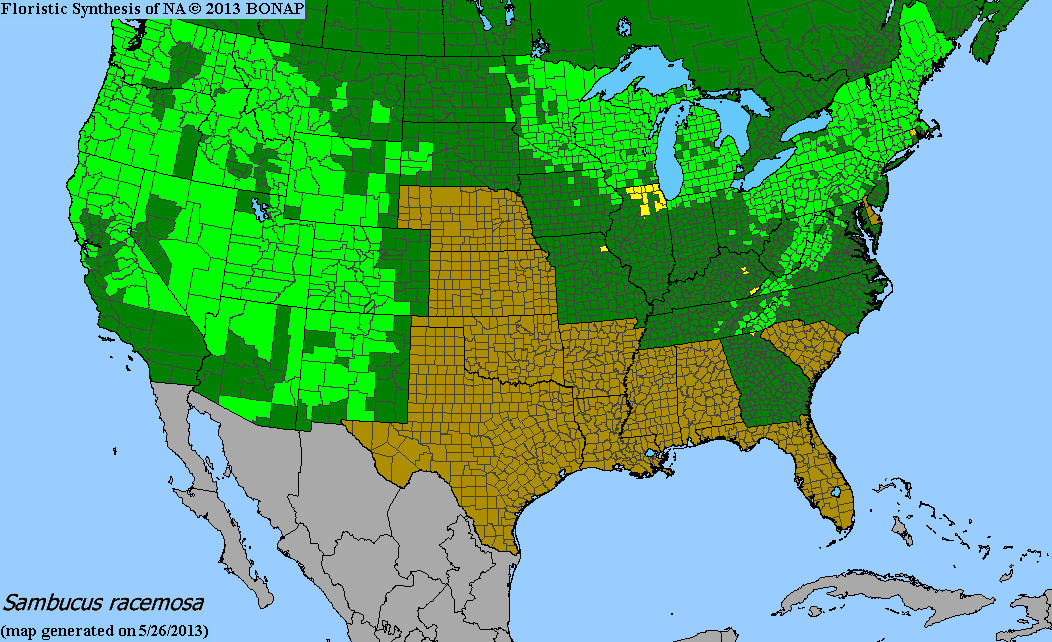
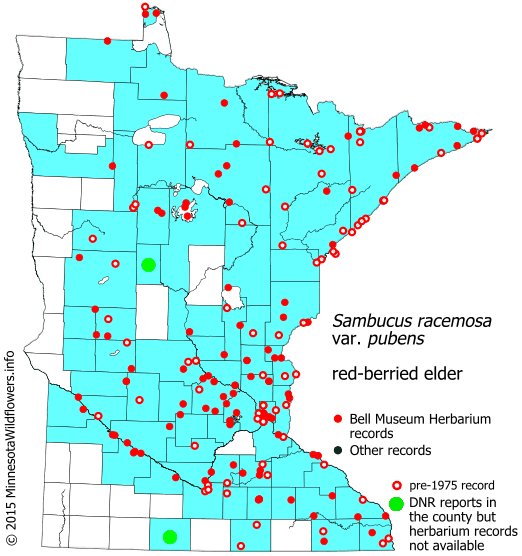
Native Range:
Red-berried elder has an expansive range the extends from the Western United States, the Midwest, and many states along the East Coast. In Minnesota, it is found throughout most of the state.
Standard Plant Information:
Plant Height:3-14'
Bloom time: April - June
Preferred Habitat: Does well in shade to full sun with average to moist soil. Often found in woodlands, deciduous or mixed forests, along shores, and wetland edges.
Planting:
Planting a tree/shrub seedling or small potted tree/shrub properly is important to ensure its healthy growth and development. Here are the steps you can follow to plant a tree:
Choose the right spot: Select a spot with adequate sunlight, water, and soil drainage. Make sure the tree has enough space to grow to its full size without interfering with other plants, structures, or utility lines.
Prepare the soil: Dig a hole that is twice as wide and slightly shallower than the root ball of the seedling. Remove weeds or debris from the area. Loosen the soil around the edges of the hole to help the roots grow more easily.
Plant the seedling: Place the seedling in the hole, making sure the top of the root ball is level with the ground surface. Gently spread out the roots and fill in the hole with soil, tamping it down lightly as you go.
Water the seedling: Water the tree/shrub deeply and thoroughly after planting, making sure the soil is evenly moist. This will help settle the soil around the roots and eliminate any air pockets.
Monitor the growth: Keep an eye on the seedling to make sure it is getting enough water and sunlight, and that it is not being attacked by pests or diseases. Prune any damaged or dead branches as necessary, and provide support if needed.
By following these steps, you can help ensure the healthy growth and development of your newly planted tree/shrub seedling.